Compression Algorithm
Time series data has a large scale and may contain a lot of redundancy, so compression methods are often used in time series databases to save storage space and reduce the I/O cost of query execution. Below, we will discuss the compression techniques used in CnosDB.
DELTA
Mainly used for timestamp, integer and unsigned integer.
Principle
First, the difference is made, that is, the first data is unchanged, other data are transformed into delta with the previous data, and all numbers are processed byzigzag, i64 is mapped to u64, specifically to zero, negative numbers are mapped to odd numbers, such as [0, 1, 2] after zigzag processing to [0, 1,2] and maximum convention numbers are calculated. After that, check if all deltas are the same, then use run-length encoding directly, which only needs to record the first value, delta, and the number of data.Otherwise, divide all delta values by the greatest common divisor (which will also be encoded into the data), and then use simple8b for encoding.
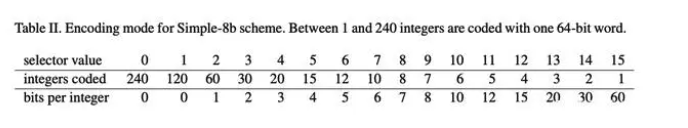
Simple 8b is a compression algorithm that encapsulates multiple integers to a 64-bit integer, the first four-bit as selector to specify the number and validity of integers stored in the remaining 60 bits, and the latter 60 bits are used to store multiple integers.In addition, when the size of delta exceeds the maximum range that simple8b can encode (exceeds 1<<60 - 1, which generally does not occur), compression is not performed, and the array is stored directly.
Applicability
In some time-consuming data, assuming that data is collected every five seconds, the time stamp is 5, that all timestamps can be restored through only three numbers, with extremely high compression, while some delta does not guarantee consistent scenarios, i.e., where using Simple 8b, are more suitable for smaller, floating data.
In the absence of specifying compression algorithms, we default to this compression algorithm for timemarks, integers, and unsigned integers, and both the compression rate and efficiency are relatively high.
GORILLA
Mainly used for floating point type.
Principle
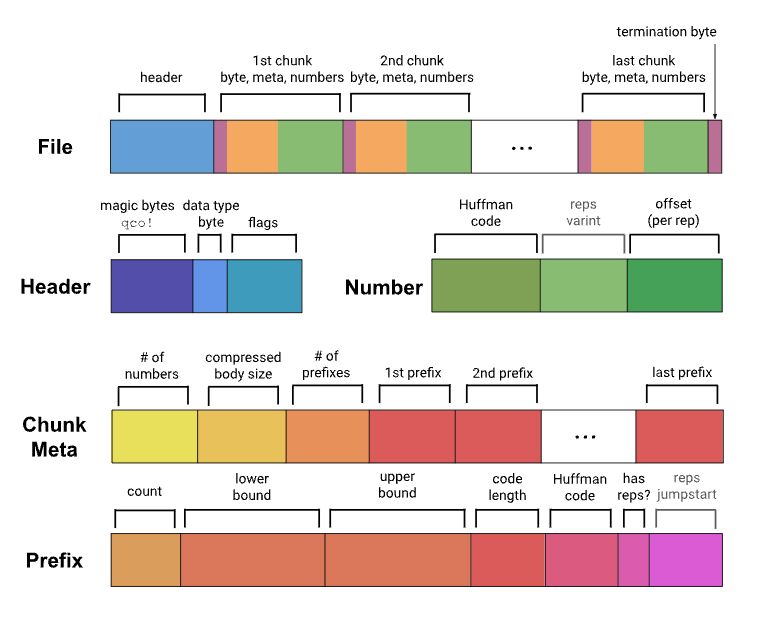
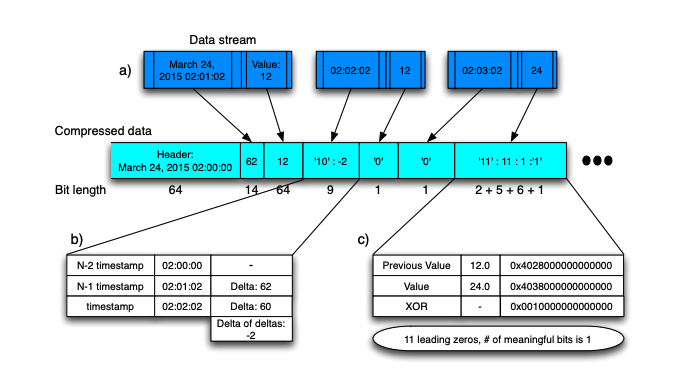
The principle of gorilla is similar to differential encoding, the difference is that differential encoding is the difference between two data, while gorilla is XOR.The first data is not processed during encoding. Calculate the XOR of the data with the previous data. If the XOR value is 0, it means it's a repeat of the previous data, so only store a single zero bit.If not zero, calculate the number of leading zeros and trailing zeros of the XOR value. If the number is the same, store the prefix 10 plus the effective bit data.If the number of elements is different, store the prefix 11 followed by the quantity of leading zeros (5 digits) and the quantity of trailing zeros (6 digits), then store the effective data bits.
The example provided in the paper:
Applicability
Compared with the delta type, it is also suitable for time series data scenarios. We may collect data in different locations, but the data collected at the same location generally has a certain level of stability. In this scenario, both the compression rate and efficiency are relatively high.
In the absence of specifying compression algorithms, we specify this compression algorithm for floating point type by default.
Pco
Mainly used for timestamps, integers, unsigned integers and floating points.
Principle
Pco performs entropy encoding on the raw data using tANS algorithm.The tANS algorithm is a modern entropy coding technique, which is a specific form of ANS (Asymmetric numeral systems).tANS uses a finite state machine, where each state corresponds to a possible outcome of encoding.The state transition depends on the symbol to be encoded, which allows it to be adjusted according to the probability distribution of the symbol.Compared with traditional Huffman coding, tANS can provide higher compression ratios when dealing with uneven symbol probability distributions.The specific principle of tANS can be referenced in this article: Streaming Asymmetric Numeral System Explained.The storage format of Pco can refer to this document: Pco-Format.
Applicability
Compared to the delta algorithm and the gorilla algorithm, the compression efficiency of the Pco algorithm is relatively low due to its more complex encoding method. There is roughly the same choice of applicable data because they all use difference algorithms. However, the quantile algorithm has a compression efficiency that is about 5 to 10 times lower. In contrast, the compression ratio is slightly better than the delta and gorilla algorithms. Below are the compression effects of various algorithms on the test data set (the compression effects on different data sets may vary).
500M floating point numbers
| Compression ratio | Compress Time | Decompress Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
Gorilla | 4.50 | 13.652 µs | 70.830 ns |
Pco | 32.97 | 1.7491 s | 9.0485 ms |
500M integers
| Compression ratio | Compress Time | Decompress Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
Delta | 13.28 | 2.8366 ms | 58.428 µs |
Pco | 35.04 | 936.65 ms | 546.99 µs |
BITPACK
Mainly used for Boolean types.
Principle
The size of a bool-type data is a byte, and for the information that bool represents, it's only one bit to represent so that we can assemble eight bool-type data into one byte.
Applicability
No matter what data, we can ensure a compression ratio of nearly eight times that we specify this compression algorithm for the Boolean type by default without specifying the compression algorithm.
String Compression Algorithm
The compression ratios of the string compression algorithms currently supported are as follows:
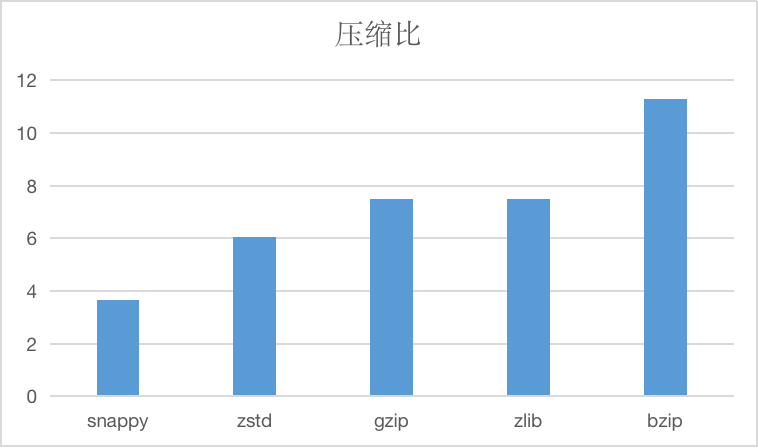
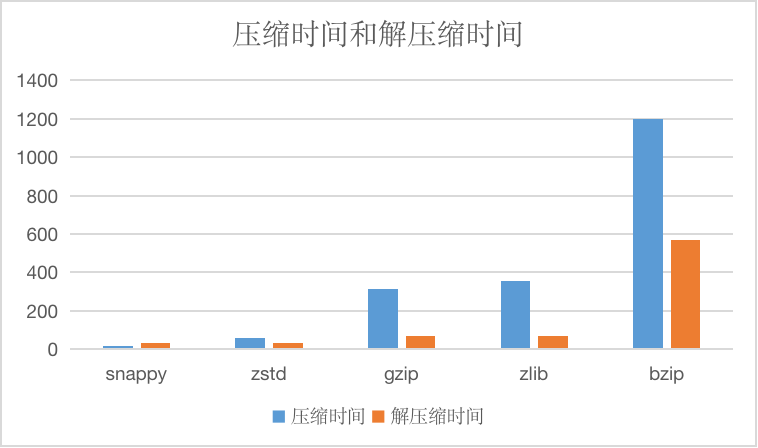
And compressed time and decompression time, units are us.
SNAPPY
Snappy algorithms are not intended to be compressed to the maximum extent and are not intended to be compatible with any other compression.On the contrary, its goal is very high compression efficiency and reasonable compression ratio, so it is recommended to use snappy in cases where efficiency is needed more.
In the absence of specifying a string compression algorithm, we specify this compression algorithm by default.
ZSTD
zstd supports multiple compression levels, and CnosDB currently uses the default compression level.
Zstd, known as Zstandard, is a fast compression algorithm that provides high compression ratios, Zstd uses a finite state entropy encoder.Provided a very powerful compromise solution for compression speed/compression ratio.
GZIP/ZLIB
gzip is similar to zlib, for the file to be compressed, it first uses a variant of the LZ77 algorithm for compression, then uses the Huffman coding method to compress the resulting output, resulting in a high compression ratio, but it is also relatively time-consuming.Both algorithms are widely used, with similar performance, and can be chosen according to the situation.
BZIP
Compared with several other algorithms, the compression rate is higher, but the compression efficiency is lower, which can be used for scenarios that require extreme compression rate, in general less recommended.
Lossy Compression Algorithm
Only Enterprise Edition supports
SDT Compression Algorithm
Mainly used for integer, unsigned integer, floating point type.
The Spinning Door Trend (SDT) is an online lossy data compression algorithm, traditionally used for supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, aimed at storing historical data for Process Information Systems (PIMs). SDT calculation has low complexity, using linear trends to represent a certain amount of data.Its most important parameter is compression deviation, which represents the maximum difference between the current sample and the current linear trend used to represent previously collected data. The principle is to determine the selection of data by examining the compressed offset coverage area formed by the current data point and the previous retained data point.If the offset coverage area can cover all points between the two, the data point is not retained; if there are data points outside the compressed offset coverage area, the previous point of the current data point is retained, and the latest retained data point is used as the new starting point.
Algorithm parameters
Deviation: a positive floating point number.It represents the maximum difference between the current sample and the current linear trend.
Dead zone compression algorithm
Mainly used for integer, unsigned integer, floating point type.
The principle of the dead zone compression algorithm is: for the time series variable data, the variable change limit (namely dead zone, or threshold) is defined. If the deviation between the current data and the last stored data exceeds the specified dead zone, the current data will be saved, otherwise the current data will be discarded.This algorithm is easy to understand and implement, and most real-time databases that use lossy compression provide this type of compression, as it only needs to be compared with the previous saved data to determine whether or not this data needs to be saved.
Algorithm parameters
Deviation: a positive floating point number.When using this algorithm, the allowed deviation is the absolute or relative value, based on the last saved number.It determines the compression rate of the algorithm, as well as the accuracy of the data after compression.