Data Sharding and Replication
CnosDB stores data in two dimensions: time-based sharding and Hash sharding.
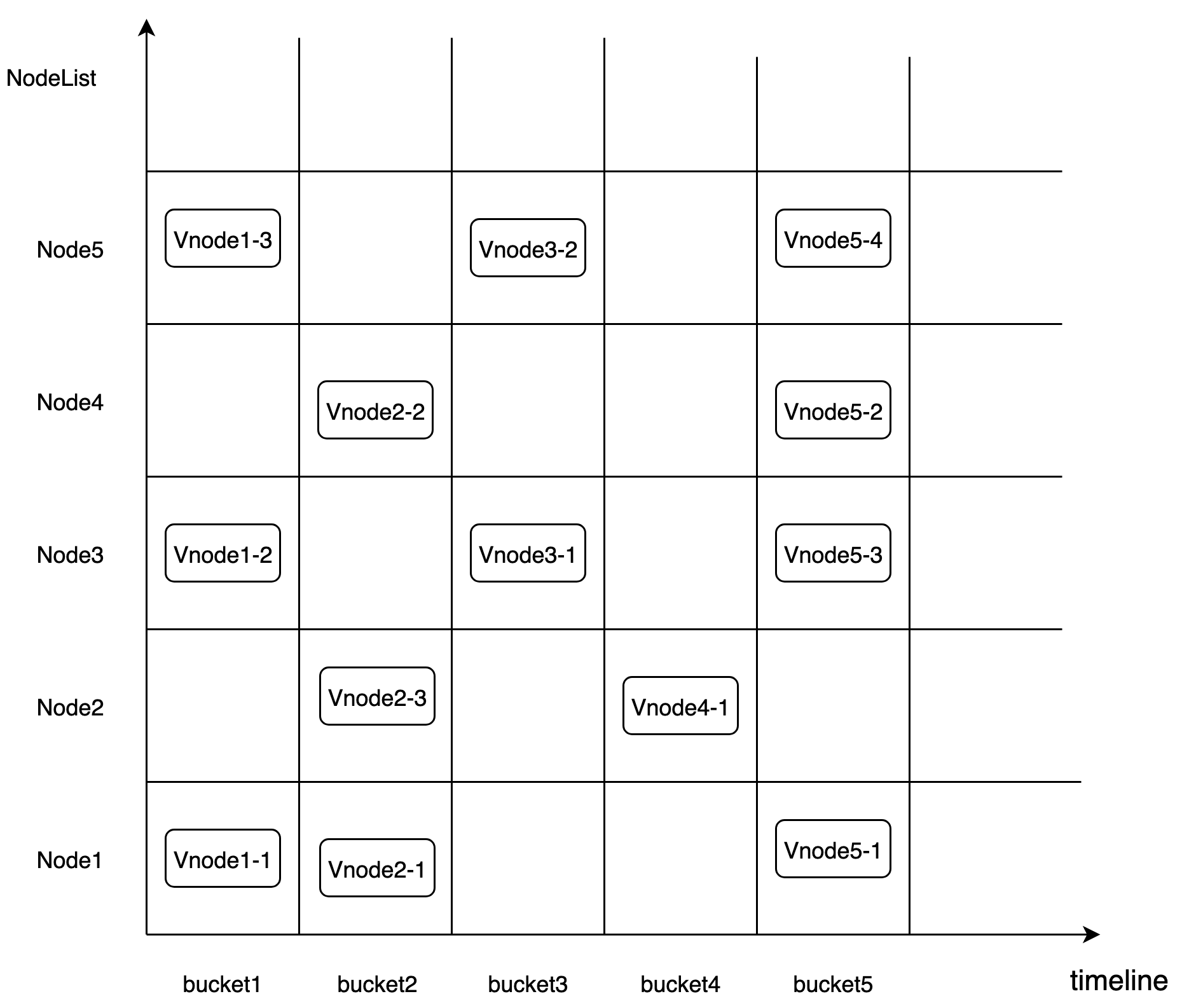
Time sharding: Due to the characteristics of time-series databases themselves, sharding by time dimension has its inherent advantages.CnosDB creates a Bucket every once in a while, each Bucket has a start and end time to store data for the corresponding time period.Whenever the system capacity is insufficient and a new storage node is added, when creating a new Bucket, the new node with the most available free capacity will be prioritized, and existing data does not need to be moved. This perfectly solves the problem of cluster expansion and data storage capacity.
Hash sharding: Time sharding perfectly solves the storage capacity problem; in a distributed cluster environment, there will be multiple machines providing services. If each bucket is only distributed on one machine node, then the write performance of the entire system is limited to a single machine.Another concept of the time-series database is SeriesKey. Hash sharding can be performed according to SeriesKey to split it into different ReplicaSets. Each replica within a ReplicaSet is called a Vnode. Each Vnode is scattered across different storage nodes. Multiple Vnodes within a ReplicaSet form a Raft replication group for data synchronization between replicas; CnosDB adopts a Multi-Raft storage solution based on ReplicaSet as a group of Raft replication groups.Vnode is the basic unit for data sharding management in CnosDB, solving the issue of system throughput by adopting the Hash Sharding method.
Bucket
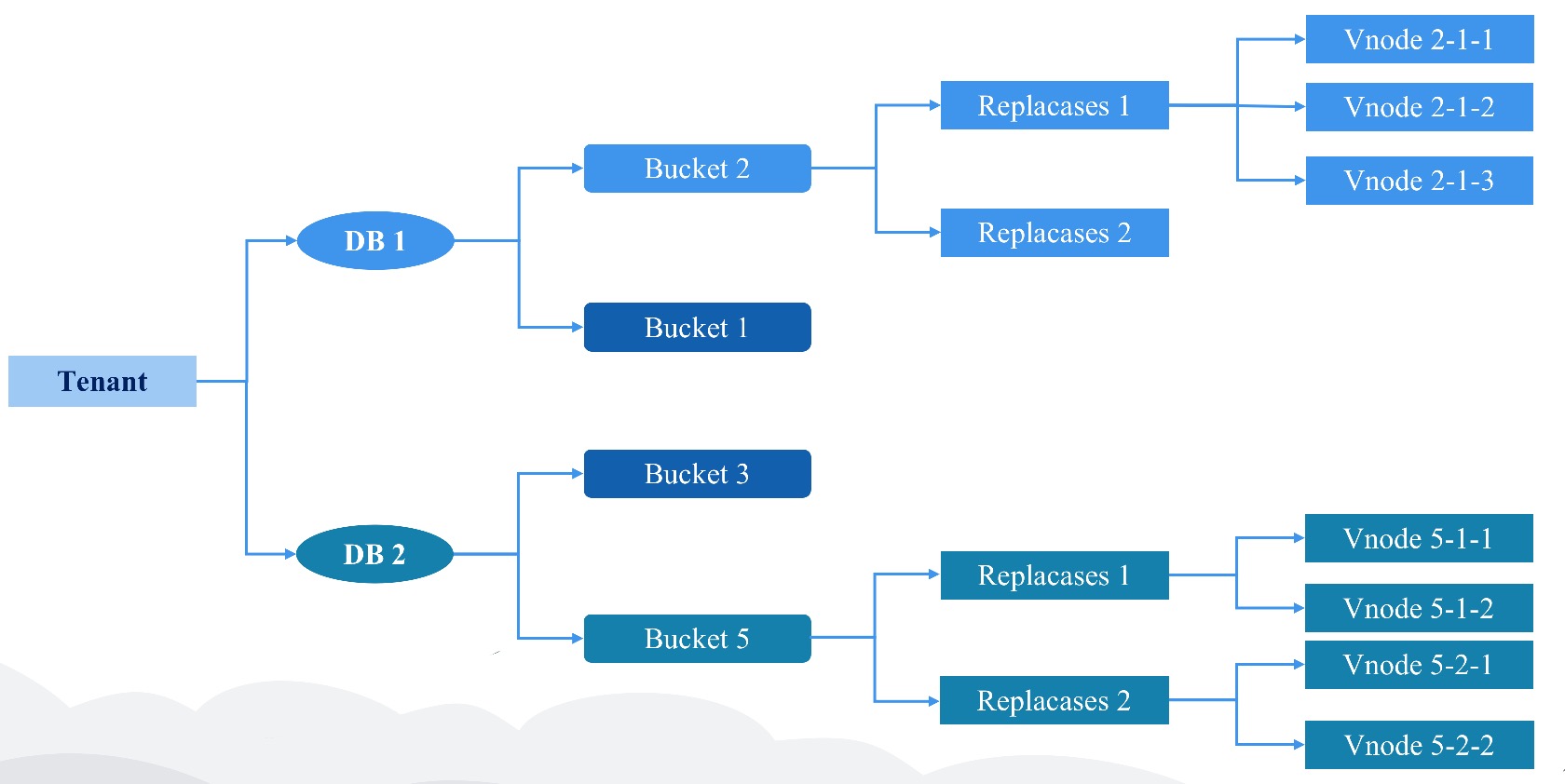
Bucket is a virtual logical unit; Bucket will create multiple shards based on user configuration to distribute data (by default, the Shard Number of data is 1).Each Bucket has the following main properties:
- Start Time
- End Time
- Database
- ReplicaSet
Vnode
Vnode is a virtual running cell and is assigned to a specific Node.Each Vnode is a Raft node, each Vnode is a separate LSM Tree, and also has its own independent WAL log.
ReplicaSet
A replication group is a Raft cluster, with each Raft node corresponding to a Vnode.
Place Rule
CnosDB supports perception data center, rack strategy, for this we designed the concept of placement rules.When creating a replica group, different replicas will be placed in different data centers and racks according to the placement rules.See details in Placement policy
Data Separation Strategy
Data from different tenants on Node are physically segmented.
/User/db/bucket/replicaset_id/vnode_id
Raft in CnosDB
Raft replication algorithm is introduced in CnosDB v2.4 version, each ReplicaSet is a Raft replication group, and the whole system runs in a Multi-Raft mode.
Data writing
- Determine which Bucket to write based on tenant, Database, and timestamp.
- According to the SeriesKey, determine which ReplicaSet to write to, that is, which Raft replication group.
- Check if the node receiving the request is the Leader if it is written directly, otherwise forward it to the Leader for processing.
Data Reading
To ensure higher data consistency during data reading, it is preferable to select the Leader node first. If it fails, the Follower node will be retried.