Storage Engine
TSKV Index and Data Storage
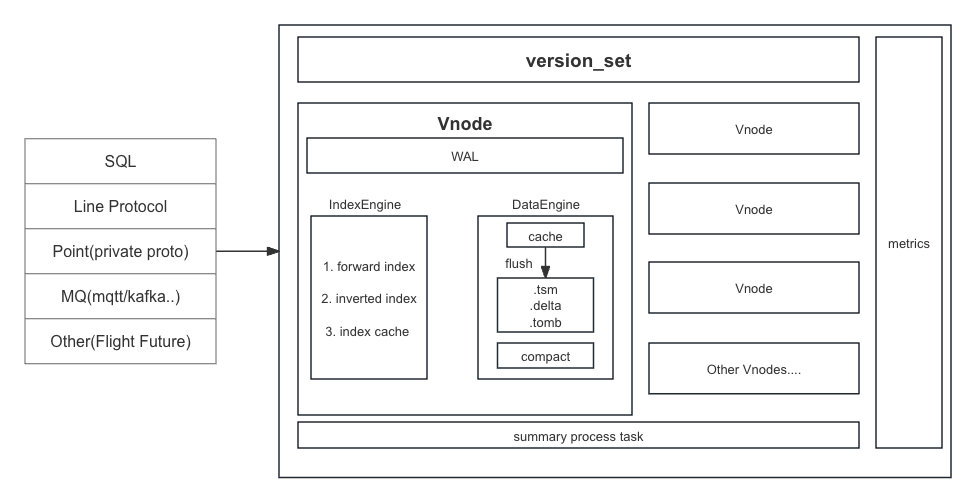
tskv is mainly responsible for storing data and indexes, and managing all vnodes on the node. Each Vnode is responsible for part of the data in a Database.There are mainly 3 blocks comprising WAL, IndexEngine and DataEngine in Vnode.
Index Engine
Indexes used to store time series data are usually models that read more and write less, mainly quickly indexing and tagkey-based conditional filtering to filter out the right series.
Main Function:
- Storage positive index.
- Storage reverse index.
- Cache index data.
Common query statements:
SELECT xxx from table where tag1= value1 && tag2=value2 [and time > aaa and time < bbb] [group by\order by\limit ....]
The design of index is mainly aimed at the where filtering conditions; used to reduce the search scale of data and speed up the query efficiency of data.
Support the following filtering conditions:
- equal to; not equal to; such as: tag = value, tag! = Value
- more than; less than; such as: tag < value
- Prefix matching; such as: tag=aaa_*
- Regular expressions; such as: tag = aaa*bbb
Index construction is performed when data is written.Most of the time series database is indexed to each tag and multiple tag sets to a series key.
Although time-series databases are write-heavy and read-light, the use of indexes during data writing is more for reading than for building. Time-series databases primarily sample and write data points for the same series at different timestamps, so the index information for each series only needs to be constructed during the first write. Subsequent writes only check for the existence of the series (a read operation) and do not require further index construction.
Index Data
- SeriesID: Each Vnode has an incrementing variable incr_id starting from 0. When a certain SeriesKey is written for the first time, incr_id increments by one, and the value of incr_id represents the SeriesID of this series.
- SeriesKey: Consists of table name and tag key-value pairs.
Index Data Structure
- HashMap\<SeriesID, SeriesKey>: Used to retrieve SeriesKey based on SeriesID.
- HashMap\<SeriesKeyHash, SeriesID>: SeriesKeyHash is the hash value of SeriesKey, which is used to obtain SeriesID through SeriesKeyHash.Mainly used to retrieve SeriesID based on SeriesKey.
- HashMap\<TableName, HashMap\<TagKey, BtreeMap\<TagValue, RoaringBitmap\<SeriesID>>>>: Inverted index, get all SeriesID based on the given TableName, TagKey, and TagValue.
Both index data and index data structure will be constructed based on the input data when writing.
Data Engine
Each DataEngine serves as a Node for data storage, with data stored on multiple Vnodes on each Node, and each Vnode responsible for part of the data in a Database.With backup in place, the mutually backup Vnodes distributed across multiple Nodes maintain data consistency through the Raft protocol.
Each Vnode is an LSM Tree used to store time-series data, and each Vnode also acts as a Raft node. So each Vnode is mainly composed of the following modules in design
WAL module
The WAL module has two main functions
- As the Write Ahead Log module of LSM Tree, used for persisting data.
- As the Raft Entry Log module of the Raft protocol, it is used to persist the logs of the Raft protocol.
When writing data, first write the data to WAL, then write it to the memory cache of VnodeState. When the Node crashes, the memory data can be recovered through the WAL, as well as the Raft state.
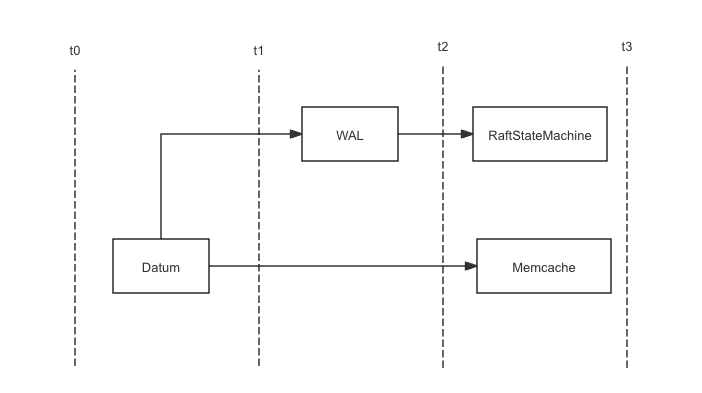
VnodeState module
The VnodeState module is the memory cache of the LSM Tree, which also stores the metadata information of the LSM Tree on the disk, such as the disk level of the LSM Tree, the TSM file location, the cache of TSMReader, etc.It is also the place where the Raft protocol state machine is actually executed. When the log of the Raft protocol is committed, the corresponding operation will be executed on VnodeState.
Summary module
Summary is the metadata file generated by the TSM file version change, which can be understood as the LSM Tree metadata of VnodeState.Used to restore information related to LSM Tree in VnodeState during downtime. Whenever there is a file version change, version change metadata
version_editwill be generated and stored in the summary file.The node will generate a large summary file after running for a long time, and we will regularly consolidate the summary file.Reduce downtime recovery time.TSM module
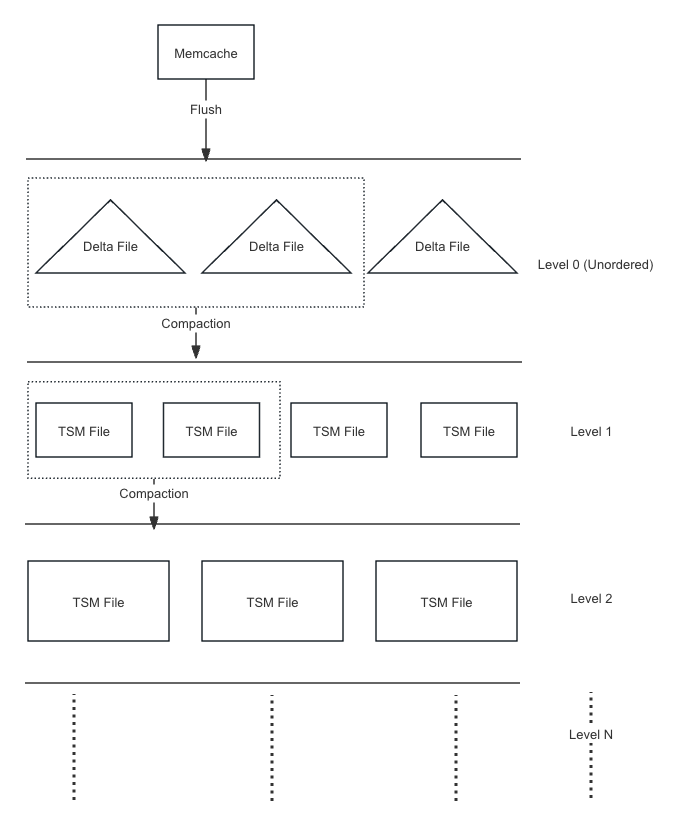
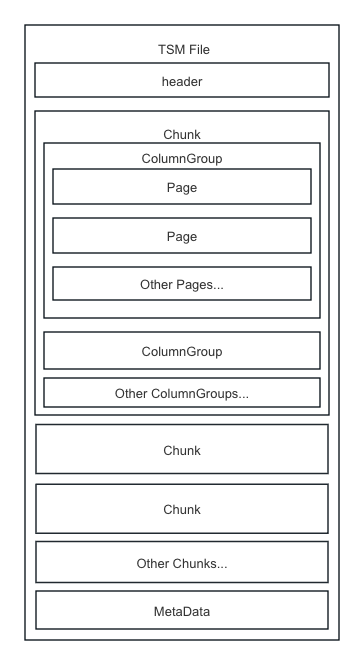
The TSM module mainly focuses on the design of TSM files.Each TSM file contains multiple Chunks. To ensure that the reading is not too amplified, each Chunk is divided into multiple ColumnGroups by line count. Each ColumnGroup contains multiple Pages, with Page being the smallest read unit, storing partial data of a column.The reading of TSM files is done in the order of Chunk -> ColumnGroup -> Page.The end of the file stores the metadata of the file, such as the file's version number, file size, and some index information of the current file data.
Compaction module
Flush
When VnodeState memory reaches the threshold specified in the configuration file, a flush operation is triggered to package the data in memory into a flush request, which is then sent to the thread responsible for processing flush requests and written to the TSM file.At the same time, the corresponding
version_editwill be generated and stored in the summary file.The Flush process divides the memory's Memcache into series, converts it into DataBlock, encodes the DataBlock into Chunk, and then writes the Chunk into the TSM file.
compaction
Every once in a while (time span configured in the Config file), and when a Flush request ends, it will start checking if compaction is needed.When there are too many files at the same level, merge multiple TSM files at the same level to create a new TSM file and store it in the next level.
The purpose of the compaction module is:
- Aggregate small tsm files to generate larger tsm files.
- Clean up files that have expired or marked to delete.
- Reduce reading and magnify, maintain the metadata related to hierarchy in VnodeState.