Architecture
Developed in the Rust language, CnosDB 2.0 provides users with an excellent time-series database that builds a complete DBaaS solution thanks to its excellent security, high performance, and strong community support.
Main features below:
Extensive: Theoretically supported time series has no limit, completely solves the problem of time series expansion, and supports cross-river expansion.
Calculate storage separation: Calculating nodes and storage nodes, can expand and shrink capacity independently and on a second scale.
Storage performance and cost: High performance storage stack, supporting hierarchical storage using cloud discs and object storage.
Query engine supports vectorized queries, providing a rich set of time series calculation functions.
Supports multiple time series protocols to write and query, providing external component import data.
Cloud side synergizes to provide the ability to fuse side ends with public clouds.
Native support for multi-tenancy, limiting tenant resource usage through quotas.
Support cloud native, support the full use of cloud infrastructure to integrate into cloud native ecology.
Introduction
The CnosDB architecture consists of two types of processes comprising: cnosdb server (cnosdb) and cnosdb meta (cnosdb-meta).Support online horizontal expansion, allowing dynamic adding nodes and having metadata and data backups to ensure cluster stability.In addition, CnosDB supports most SQL syntax and users can easily access and import data via cnosdb-cli client connections.
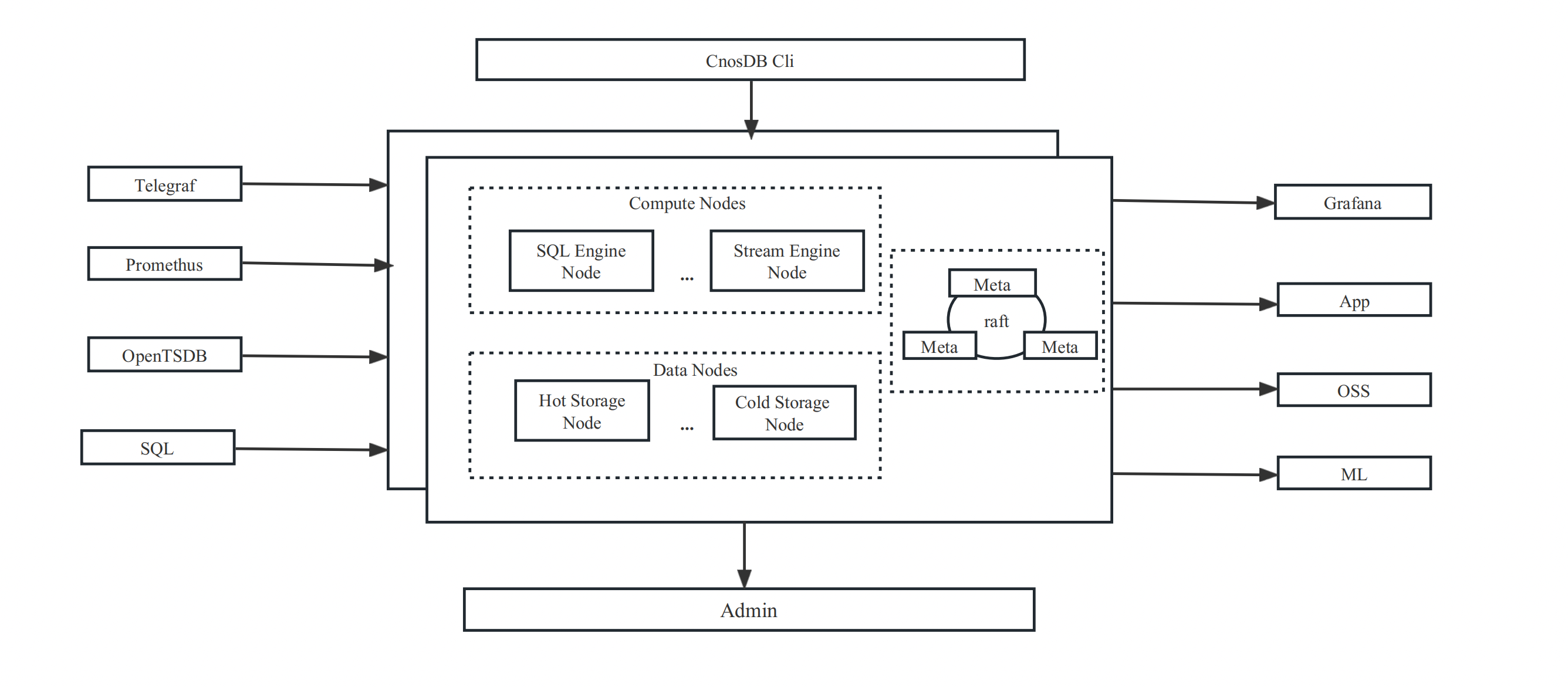
CnosDB
Vnode: A Vnode is a logical computing unit distributed to a specific Node, and it is also the smallest unit for data replication.cnosdb is internally divided into two services: query and tskv services, which are at the core of cnosdb.
Query: querying service, Stream Query Service, mainly responsible for sql parsing, query optimizations and physical plan execution.Users can flexibly configure whether the Query node starts in stream processing mode, and can flexibly configure the processing mode of the Query node according to their own business needs.
Tskv: the storage service is mainly responsible for the storage of indexed and temporal data and data reading and filtering. tskv can be configured as a cold data node and a hot data node, and the data will be automatically migrated from the hot data node to the cold data node according to the cooling time to balance the storage performance and cost see [Tiered Storage](/docs/manage/tiered_ storage.md).
ConsDB Meta
cnosdb meta, the corresponding program is named cnosdb-meta, which is used to maintain the consistency of the cluster.It stores metadata in the cluster, including information on tenants, user role information, topology, replica distribution, and data distribution within the cluster. The cnosdb meta cluster is based on a Draft Cohesion Consensus agreement and is usually proposed to deploy 2n+1 cnosdb-meta service to ensure high cluster availability.
CnosDB makes the following optimizations in the meta cluster:
Cache and localize frequently accessed data.
After the schema information is stored locally, subscribe to the schema version changes from the meta cluster to relieve the read pressure on the meta cluster.
The meta cluster shares the leader pressure and provides a Follower/Read solution to optimize the read performance.
Data management
CnosDB Cli is a self-carried command line tool used to connect CnosDB for SQL queries and line protocol file imports.
CnosDB supports multiple writing protocols such as: SQL line protocol, opentsdb, Prometheus, eslog. Different interfaces will also be used for different protocols such as trace in the future. Each protocol can be enabled or disabled according to configuration to meet user needs.
Grafana is an open-source data visualization tool that supports multiple data sources, and CnosDB provides Grafana Plugins and users can use Grafana plugin for data visualization and warning via CnosDB connections.
CnosDB supports JDBC connections. Users can search data via JDBC connection to CnosDB.
CnosDB provides a complete set of Restful API interfaces, users can query and write data through Restful API.
CnosDB provides a python SDK that allows users to integrate with machine learning systems through the python connector.
CnosDB supports writing multiple agents such as telegraf, vector, filebeat, etc., users can write data into CnosDB through configuring agents.
CnosDB Admin is an enterprise version tool that provides visual monitoring and management of clusters, offering cluster monitoring, alerts, log viewing, cluster configuration, cluster scaling, and other functions, making it easier for enterprise users to manage and operate multiple clusters.
The ecosystem tools of CnosDB are still being further enhanced. See CnosDB Ecosystem Tools
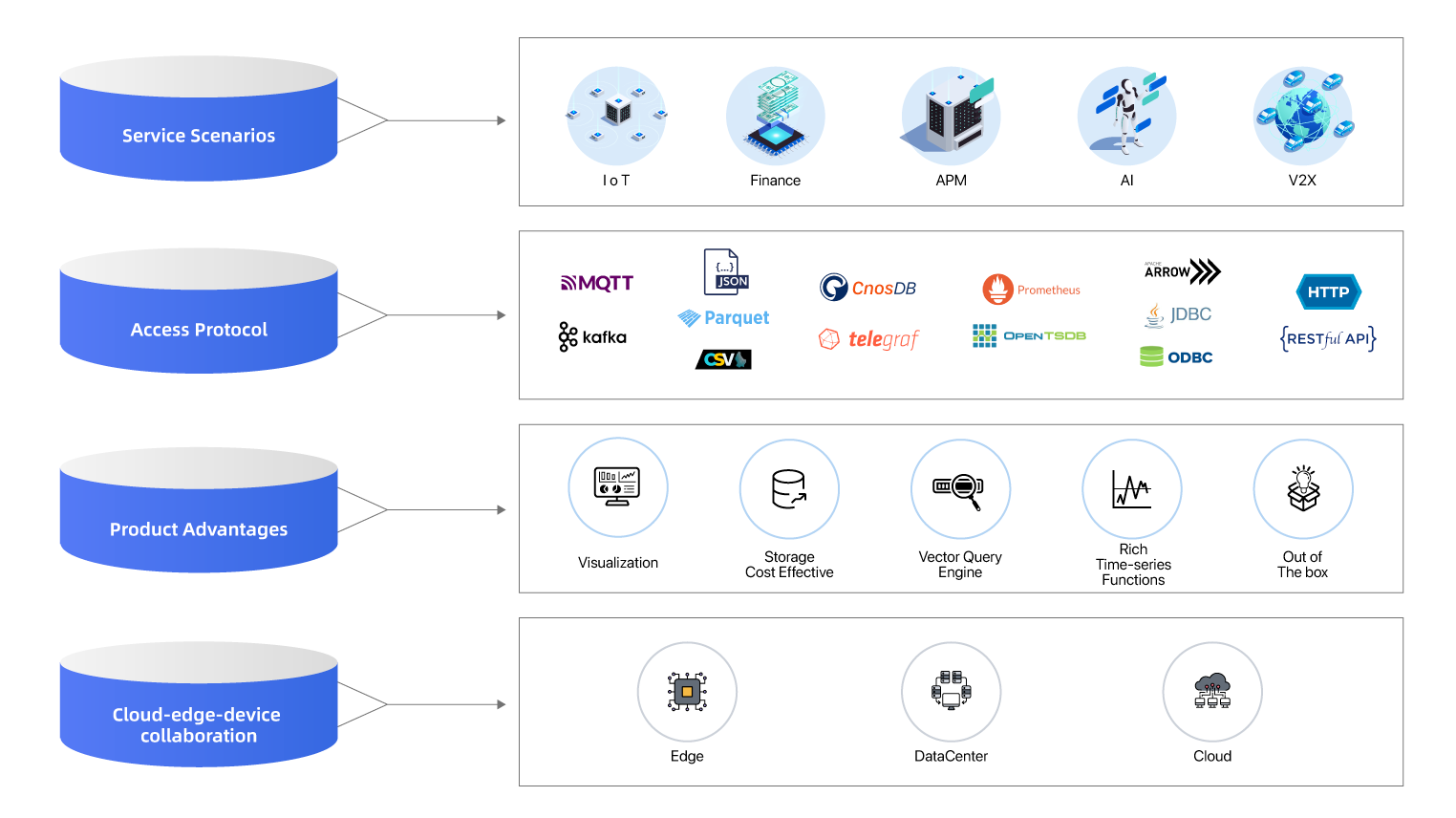
Deployment Mode
CnosDB supports multiple deployment modes: standalone, distributed, storage-compute separation, storage-compute integration. These flexible deployment modes can meet the deployment needs of users in various complex scenarios.
cnosdb run -M singleton
cnosdb run -M query
cnosdb run -M tskv
cnosdb run -M query_tskv
Data separation
query layer
In DataFusion, the isolation relationship of catalog is divided into
catalog/schema/table.We use this isolation, which we use to split the segregation relationship betweentenant/<namespace>/database/table.table Corresponds to a table in a specific database that provides a schema definition and implements TableProvider.
database manages multiple tables corresponding to one of the specific databases.
namespace corresponds to this catalog.Each tenant holds a catalog only, different databases are seen by different tenants, and different tenants can use the same database name.When a user login, a session will get TenantID, so you see your default namespace, resulting in soft isolation.
tskv layer
Catalog split policy referred to in the above presentation for
/tenant/db/vnode_id, data partition rules see Data sharding and replicationEach Node node has an instance called tskv, which keeps all Vnode information on the current Node.Each Vnode data is saved in a separate directory.Manage the life cycle of data based on TTL parameters in the database.In addition, such a strategy would facilitate statistical data cataloguing in order to account for renters.