Cloud Native
Cloud-native technology helps organizations build and operate applications that can be elastically scaled in new dynamic environments such as public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.Representative technologies of cloud-native include containers, service mesh, microservices, immutable infrastructure, and declarative API. These technologies can build loosely-coupled systems with good fault tolerance, easy management, and ease of observation.By combining reliable automation means, cloud-native technology enables engineers to easily make frequent and predictable major changes to the system. From CNCF
Advantage of Cloud Native Database
High scalability.
High scalability, i.e., more flexible database expansion and contraction capabilities, cloud-native database using resource decoupling approach, distributed storage of data and separation from cloud computing facilities, when the traffic increases to meet the demand for expansion, when the traffic decreases to avoid waste of resources for capacity reduction.The characteristics such as distributed storage, resource decoupling, and ecosystem compatibility also increase the portability of cloud-native databases.
Usability and Stability
Ease of use is reflected in the cloud deployment of cloud-native database computing nodes, because the function is integrated in the cloud, the user only needs to access the use of the interface through the front-end; stability is more reflected in the distributed storage of data, distributed storage greatly reduces the impact of a single point of failure on the server, the data is also more secure.
Cost savings
The traditional coupling of database storage and computation requires a large number of individually packaged hardware devices, which means a significant investment in hardware and the need for maintenance by dedicated personnel.In addition, the expenses incurred in maintaining and expanding servers are also quite substantial.And the cloud database is not only low-investment but also more cost-efficient in terms of database maintenance and expansion.
CnosDB Cloud-native
CnosDB itself has gone through the development process from monolithic to distributed, supporting the architecture of singleton, storage-computing integration, and storage-computing separation.
Operator
Architecture
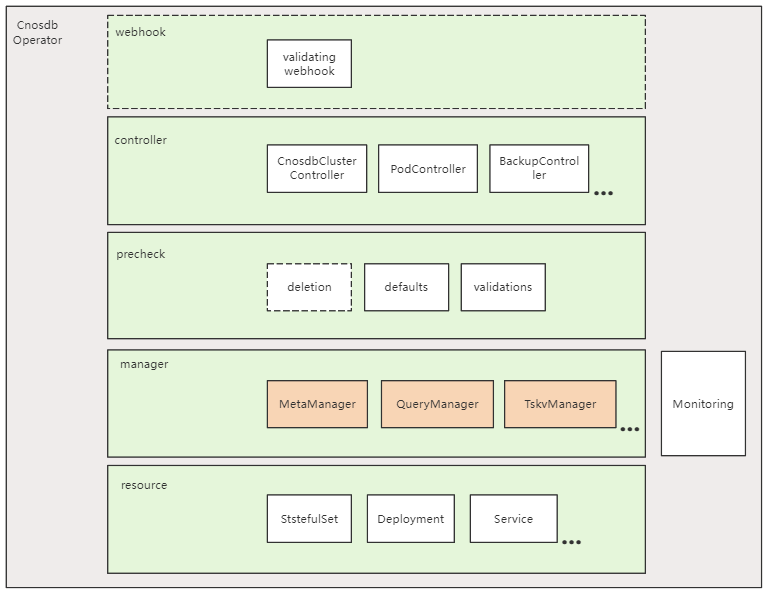
The architecture of CnosDB-Operator is based on the Kubernetes Operator pattern, including the following core components:
CRD (Custom Resource Definition): defines the specifications and schema of CnosDB resources.
- CnosdbCluster: Used to describe the desired CnosDB cluster for the user.
- CnosdbBackup: Used to describe the backup work expected by the user.
- CnosdbBackupRecover: Used to describe the backup recovery work expected by the user.
Controller: responsible for monitoring and managing CnosDB resources.It performs create, update, and delete operations based on the status and specifications of resources to ensure the consistency and correctness of the CnosDB cluster configuration.
The architectural diagram is as follows:
How it works
The flow chart is as follows:
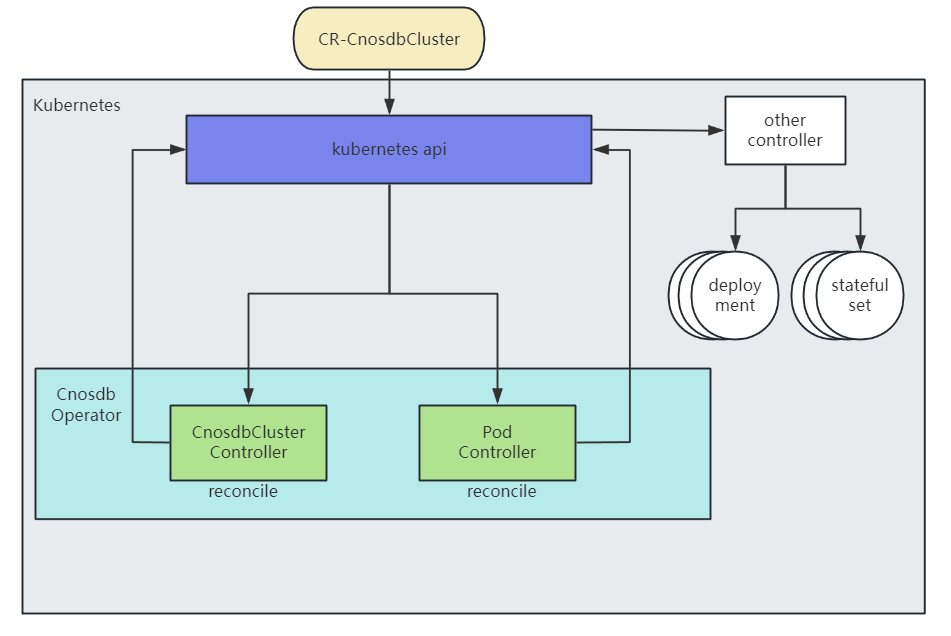
As shown in the figure, the operator takes the user-defined CR as the final target, continuously interacts with the k8s api by monitoring changes in cluster resources, and ultimately brings the resources in the cluster to the desired operational state of the user.
Feature
- Deploy
When a user creates a CR for a CnosdbCluster, the Operator will create a cluster instance based on the CR configuration.Supports deployment modes such as monolithic, storage computing integration, and storage computing separation.
- Expansion/scaling
Expansion/Scaling supports two modes: horizontal and vertical.Horizontal scaling is achieved by modifying the number of replicas in the CR.Vertical scaling involves modifying the quantity of resources required by nodes in the CR.Based on the features provided by CnosDB, it is more convenient to achieve secure downsizing, ensuring data integrity.
- Fault automatic migration
The Operator will continuously monitor the deployed CnosDB cluster.When the operator detects changes in the pod, it triggers tuning for the corresponding type of pod based on the pod's type.Pod tuning can be divided into meta, query, and tskv tuning.
- Backup and restore
By creating BackupTask and Restore CRs, backup and restore functions can be implemented respectively.Backup strategy supports manual trigger and scheduled backup.Backup and restore support both local and remote (e.g. s3) scenarios.
- Monitoring Alarm
After enabling the monitoring alarm function, Prometheus will collect and monitor various performance metrics in the CnosDB cluster, including the number of healthy pods, cluster uptime, number of failover incidents, and parameters such as CPU, memory, and disk related to the cluster.
cnosdb-cloud
Both helm and operator are cloud-native deployment methods supported by CnosDB, suitable for users to deploy privately, whether it is their own built k8s cluster or private cloud.At the same time, CnosDB has also developed a cloud project deployed on the AWS public cloud for interested users.Provide users with the Baas usage environment of the CnosDB project: https://cnosdb.cloud.
Advantages:
Provide users with the opportunity to try CnosDB to avoid the troubles of configuring the environment.
For users with small data volume requirements, a lower-cost CnosDB solution is provided.