Compression Algorithm
时序数据规模很大,且可能存在大量冗余,因而在时序数据库中经常使用压缩方法来节约存储空间和查询执行时的I/O代价,下面将讨论一些时序数据库中常见的压缩技术。
不同时序数据库的具体存储结构与压缩算法在设计上相差很大。以Open TSDB为代表的分布式时序数据库底层依托HBase集群存储,存在基本的时序数据模型,根据时序数据的基本特征对时序数据进行压缩存储。Open TSDB使用类字典压缩算法,通过将索引名称和每个序列名称的每个标签,通过进行编码来减少序列内存使用。然而依然存在很多无用的字段,无法有效的压缩,聚合能力比较弱。InfluxDB具有更丰富的数据类型,InfluxDB在整型数据采用整型编码,整数编码的压缩具体取决于原始数值的范围。时间戳为独立的数据类型,并且具有一定的规律可循,在InfluxDB中,针对时间戳数据先执行排序操作后使用delta算法进行编码,然后再根据编码结果采用不同的算法进行处理。有关 CnosDB 的压缩算法,下面的内容将帮您对其有更清楚的了解。
DELTA
Mainly used for timestamp, integer and unsigned integer.
Principle
First, the difference is made, that is, the first data is unchanged, other data are transformed into delta with the previous data, and all numbers are processed byzigzag, i64 is mapped to u64, specifically to zero, negative numbers are mapped to odd numbers, such as [0, 1, 2] after zigzag processing to [0, 1,2] and maximum convention numbers are calculated. Then judge that if all deltas are the same, use the cruise path code directly, that is, only the first value, delta, and the number of data. Otherwise, all delta values are divided into maximum convention numbers (maximum convention numbers are encoded into data), and then encoded using Simple 8b.之后判断一下如果所有的delta都相同,就直接使用游程编码,即只需要记录第一个值,delta和数据的数量。Compared with the delta algorithm and the gorilla algorithm, because the difference algorithm is also used, it is roughly the same in the selection of applicable data.
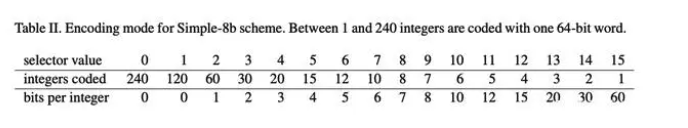
Simple 8b is a compression algorithm that encapsulates multiple integers to a 64-bit integer, the first four-bit as selector to specify the number and validity of integers stored in the remaining 60 bits, and the latter 60 bits are used to store multiple integers. In addition, when delta is larger than the maximum range of Simple 8b energy encoding (more than 1<60-1, generally not) does not compress and stores arrays directly.The Revolving Door Trend (SDT) is an online lossy data compression algorithm traditionally used in Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems designed to store historical data of Procedural information Systems (PIMs). SDT has low computational complexity and uses a linear trend to represent a certain amount of data. Its most important parameter is the compression deviation, which represents the maximum difference between the current sample and the current linear trend used to represent the previously collected data. The idea is to look at the compression offset coverage between the current data point and the previous retained data point to decide which data to choose. If the offset coverage area can cover all points in between, the data point is not retained. If a number of points fall outside the compression offset coverage area, it is retained when The previous point of the previous data point and take the latest retained data point as the new starting point.
Applicability
In some time-consuming data, assuming that data is collected every five seconds, the time stamp is 5, that all timestamps can be restored through only three numbers, with extremely high compression, while some delta does not guarantee consistent scenarios, i.e., where using Simple 8b, are more suitable for smaller, floating data.
In the absence of specifying compression algorithms, we use this compression algorithm for timemarks, integer and unsigned integers, and the compression rate is higher.
GORILLA
Mainly used for floating point type.
Principle
The principle of Gorilla is similar to the difference, the difference is that the difference is the difference between two data, and gorilla is different or different. The first data is not processed at the time of coding, and if the previous data is different from the previous data, if the difference or value is 0, repeat it with the previous data, write a patch to represent repetition, and, if not zero, calculate the first zero and back derivative zeros of the heterogeneous or value delta. If the number is the same, only the intermediate valid bit is encoded. If the number is different, the first 0.5 bits are derived, the back 0. 5 bits are written, and then the intermediate valid bit is written.编码时第一个数据不进行处理,计算后一个的数据与前一个数据的异或,如果异或值为0,则与上一个数据重复,写一个补位用来表示重复,如果不为零,则计算异或值delta的前导零和后导零个数,如果个数相同,则只编码中间有效位,如果个数不同则前导零写5位,后导零写6位,然后再写中间有效位。
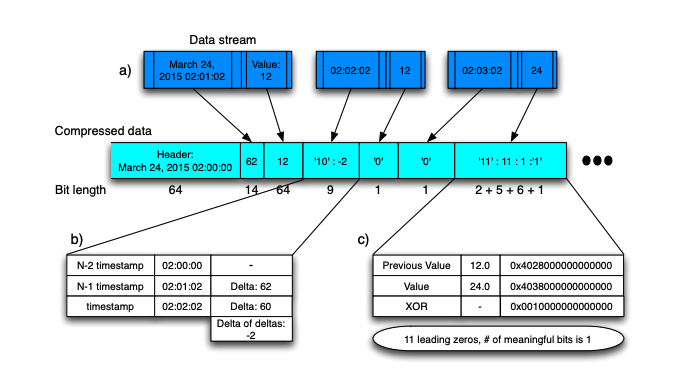
Applicability
As compared with delta type, it is also suitable for time-order data scenarios, and we may collect data in different locations, but the toponymic-related information collected at the same location is generally consistent, in which the compression rate is higher than that of compression efficiency.
In the absence of specifying compression algorithms, we specify this compression algorithm for floating point type by default.
QUANTILE
Mainly used for timestamps, integers, unsigned integers and floating points.
Principle
Qantile supports multiple levels of compression, and CosDB currently uses the default compression level.
通过哈夫曼编码和偏移量描述每个数据,用哈夫曼码对应数据所在的范围[lower, upper],偏移量指定该范围内的确切位置。Each data is described by Huffman coding and offset, and the offset specifies the exact location of the range of the data by the Huffman code corresponding to the range of the data. For each block compression, the difference processing is first carried out, the data after the difference is replaced by the current data, then the current array is divided into multiple blocks at an interval of 128, each block determines a range and associated metadata, while calculating the maximum number of conventions per block, optimizes the number of conventions as appropriate, and merges some adjacent blocks, then determines its Huffman encoding based on the weight of each block in the data, and finally encodes the data using them.
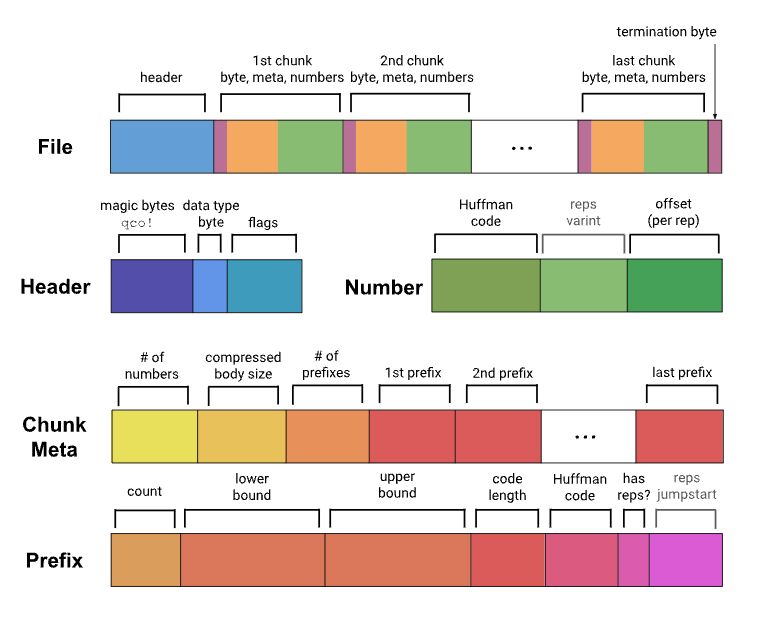
Applicability
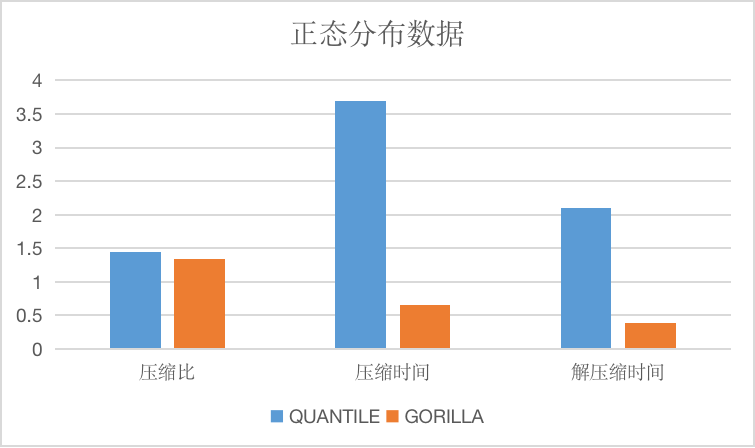
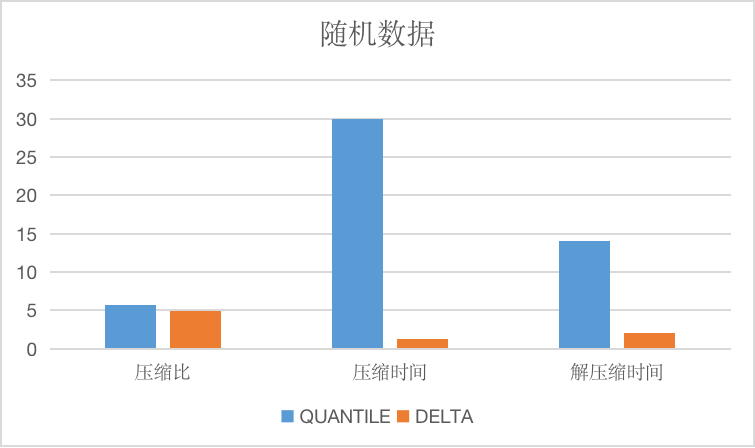
相比较于delta算法与gorilla算法,由于同样使用了差分算法,在适用数据的选择上大致相同,由于quantile算法采用了更复杂的编码方式,导致压缩效率比较低,大约有5到10倍的差距,相对地,压缩率则稍优于delta与gorilla算法。
The longitudinal axis of the image is the compression ratio, the time is only relative.
BITPACK
Mainly used for Boolean types.
Principle
The size of a bool-type data is a byte, and for the information that bool represents, it's only one bit to represent so that we can assemble eight bool-type data into one byte.
Applicability
No matter what data, we can ensure a compression ratio of nearly eight times that we specify this compression algorithm for the Boolean type by default without specifying the compression algorithm.
String Compression Algorithm
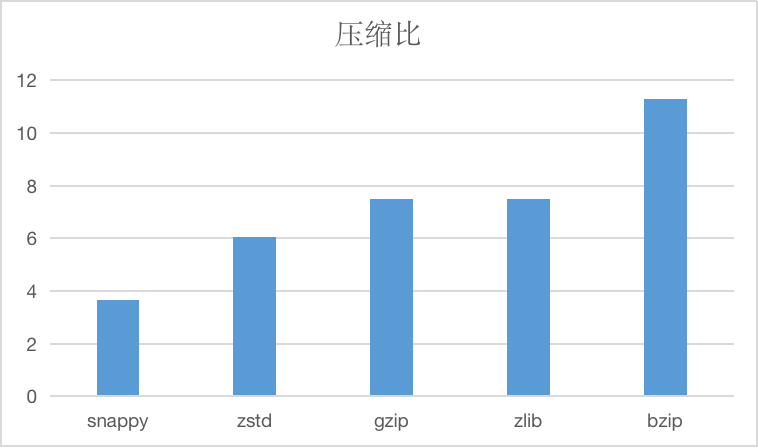
The string compression algorithm currently supported is compressed, such as below.
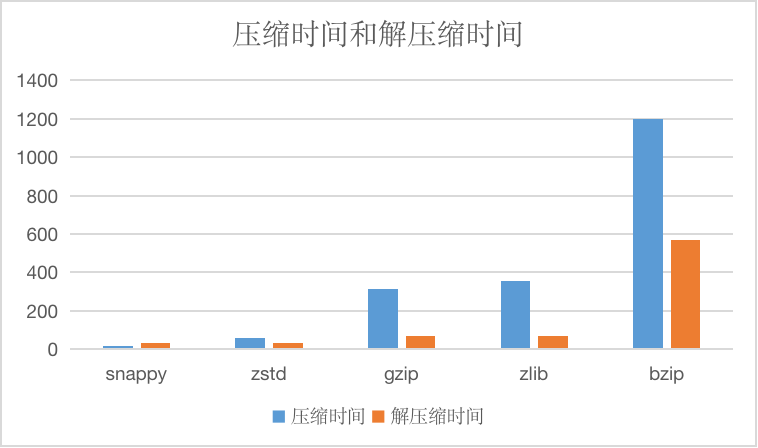
And compressed time and decompression time, units are us.
SNAPPY
Snappy algorithms are not designed to minimize compression or are not designed to be compatible with any other compression library. Instead, its goal is to be very high compression efficiency and reasonable compression rates, so it is recommended to use snappy more efficiently.相反,它的目标是非常高的压缩效率和合理的压缩率,所以在更加需要效率的情况下推荐使用snappy。
In the absence of specifying a string compression algorithm, we specify this compression algorithm by default.
ZSTD
Zstd supports multiple compression levels, and CnosDB currently uses the default compression level.
Zstd, known as Zstand, is a fast compression algorithm that provides high compression ratio, and Zstt uses a finite state entropy encoder. A very powerful compromise scheme for compression speed/compression rate is provided.提供了非常强大的压缩速度/压缩率的折中方案。
GZIP/ZLIB
Gzip is similar to zlib. For files to be compressed, a variant of the LZ77 algorithm is first used to compress the results by using Huffman coding, with high compression rate but also time-consuming. Both algorithms are widely used and have similar performances and can be selected according to the situation.这两种算法使用均比较广泛,性能相似,可以根据情况选择。
BZIP
Compared with several other algorithms, the compression rate is higher, but the compression efficiency is lower, which can be used for scenarios that require extreme compression rate, in general less recommended.