Kafka
As more and more application architectures shift towards microservices or serverless structures, the number of applications and services is increasing every day.Users can process the ever-increasing time series data either through real-time aggregation or through calculations that output measurements or indicators.In the face of massive data generated, users can capture and observe the changes in the data in the system in various ways. In a cloud-native environment, one of the most popular ways is to use events.
Apache Kafka is a durable, high-performance messaging system, also considered a distributed streaming platform.It can be applied to many use cases, including message delivery, data integration, log aggregation, and metrics.As for the indicators, simply having a message backbone or agent is not enough.Although Apache Kafka is very durable, it is not designed for running metrics and monitoring queries.This is exactly the strength of CnosDB.
In this article, we will mainly introduce how to implement a solution for real-time acquisition and storage of streaming data using Kafka+Telegraf+CnosDB in the Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS environment.In this operation, the CnosDB version is 2.3.0, Kafka version is 2.5.1, and Telegraf version is 1.27.1.
Architectural design
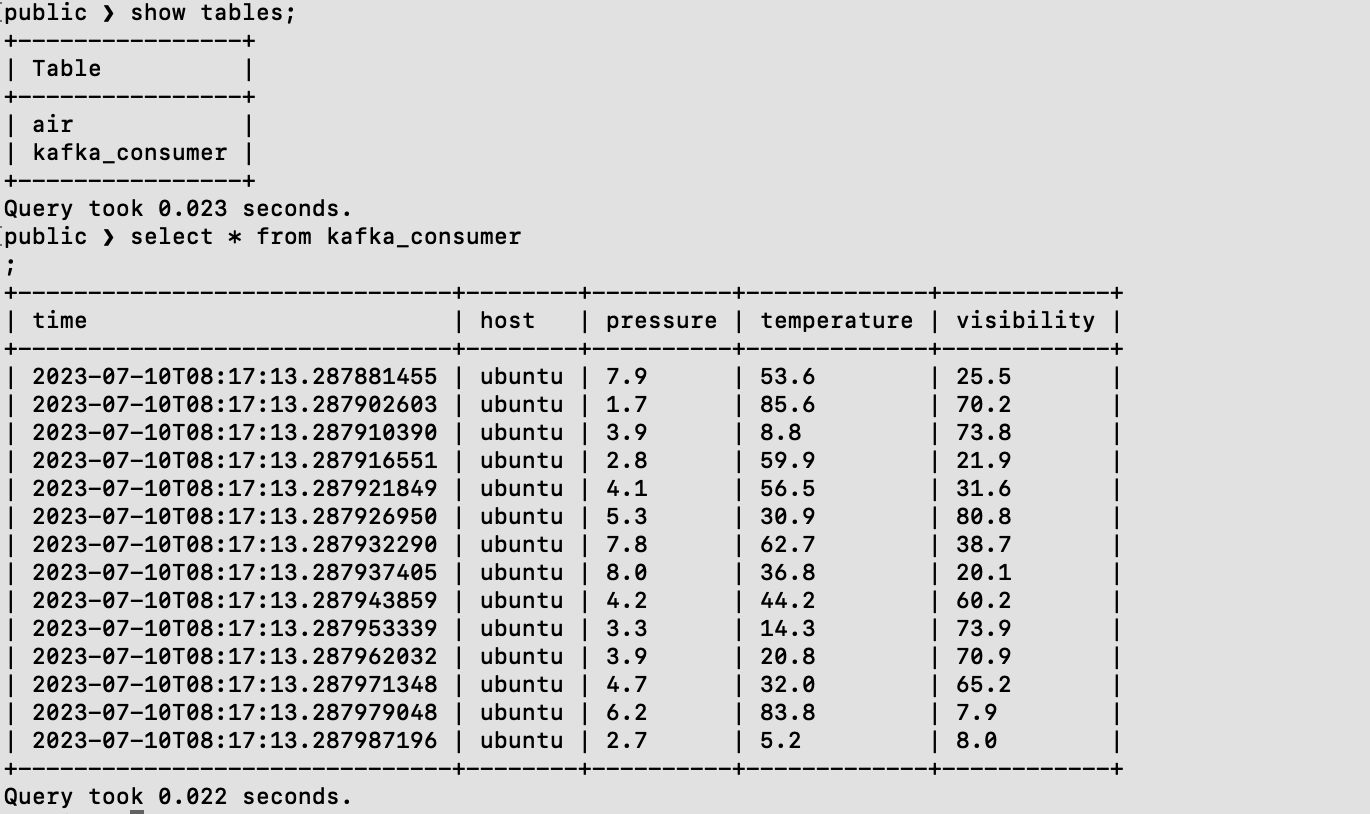
By combining Kafka, Telegraf, and CnosDB, the complete data process can be achieved:
- Data Generation: Using sensors, devices, or other data sources to generate data and send it to the Kafka topic.
- Kafka message queue: Kafka receives and stores data streams, ensuring data security and reliability.
- Telegraf Consumers: Telegraf acts as a consumer of Kafka, subscribes to Kafka topics, and retrieves data streams.
- CnosDB data storage: Preprocessed data is sent by Telegraf to CnosDB for time series data storage.
The overall application architecture is as shown in the diagram:
Kafka
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed streaming platform designed for processing real-time data streams, characterized by high reliability, high throughput, and low latency, and is currently used by most companies.Its usage is very versatile, including:
- Stream processing: It provides the event backbone by storing real-time events for aggregation, enrichment, and processing.
- Indicator: Apache Kafka has become a central aggregation point for many distributed components or applications (such as microservices).These applications can send real-time metrics for use by other platforms, including CnosDB.
- Data integration: Data and event changes can be captured and sent to Apache Kafka, and any application that needs to take action on these changes can use them.
- Log aggregation: Apache Kafka can act as the backbone of a log stream platform, transforming log blocks into data streams.
Several core concepts
- Instance (Broker): The Broker of Kafka is a server node in the Kafka cluster, responsible for storing and forwarding messages, providing high availability, fault tolerance, and reliability.
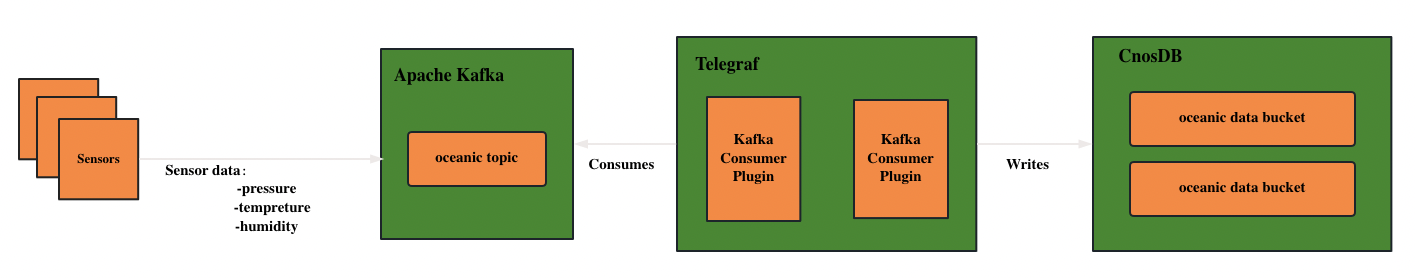
- Topic: In Apache Kafka, a topic is a logical storage unit, similar to a table in a relational database.Topics are distributed through partitions via brokers, providing scalability and resilience.
- Producer: Producers publish messages to the specified topic in Kafka.Producers can choose to send messages to a specific partition or let Kafka automatically determine the assignment strategy.
- Consumer: A consumer reads messages from one or more partitions of a specified topic.Consumers can be organized in different ways, such as unicast, multicast, consumer groups, etc.
- Publish-Subscribe Pattern: Refers to producers publishing messages to one or more topics, while consumers can subscribe to one or more topics to receive and process messages from them.
Simply put, when a client sends data to Apache Kafka cluster instances, it must send it to a topic. In addition, when the client reads data from the Apache Kafka cluster, it must read from the topics.The client that sends data to Apache Kafka is called a producer, while the client that reads data from the Kafka cluster is called a consumer.The data flow diagram is as follows:
Deploy Kafka
Download and install
- Install JDK and Zookeeper environment
sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
sudo apt install zookeeper
- Download and extract the Kafka package
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.5.1/kafka_2.12-2.5.1.tgz
tar -zxvf kafka_2.12-2.5.1.tgz
- Enter the decompressed Kafka directory
cd kafka_2.12-2.5.1
Modify the configuration file
$KAFKA_HOME/config/server.properties(modify configuration information such as ports, log paths, etc., as needed)Save and close the editor.Run the following command to start Kafka:
Kafka will run in the background and listen for connections through the default 9092 port.
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
Telegraf
Telegraf is an open-source server agent program used to collect, process, and transmit metric data from systems and applications.Telegraf supports multiple input plugins and output plugins, and can integrate with various types of systems and services.It can collect metric data from various sources such as system statistics, log files, API interfaces, message queues, etc., and send it to various targets such as CnosDB, Elasticsearch, Kafka, Prometheus, etc.This makes Telegraf very flexible and adaptable to different monitoring and data processing scenarios.
- Lightweight: Telegraf is designed as a lightweight agent, with relatively low consumption of system resources, and can run efficiently in various environments.
- Plugin-driven: Telegraf uses plugins to support various input and output functionalities.It provides a rich plugin ecosystem that covers many systems and services.Users can select the appropriate plugin according to their needs to collect and transmit indicator data.
- Data processing and transformation: Telegraf has flexible data processing and transformation capabilities, which can filter, process, transform, and aggregate collected metric data through plugin chains to provide more accurate and advanced data analysis.
Deploy Telegraf
- Install Telegraf
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install telegraf
Switch to the default configuration file directory of Telegraf, which is located at /etc/telegraf
Add the target OUTPUT PLUGIN to the configuration file telegraf.config
[[outputs.http]]
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8902/api/v1/write?db=telegraf"
timeout = "5s"
method = "POST"
username = "root"
password = ""
data_format = "influx"
use_batch_format = true
content_encoding = "identity"
idle_conn_timeout = 10
Parameters that need to be modified as needed:
Note: The remaining parameters can be consistent with the configuration example above.
url: CnosDB address and port
username: Username for connecting to CnosDB
password: Password corresponding to the username for connecting to CnosDB
- Uncomment the following configuration in the configuration file and modify it as needed
[[inputs.kafka_consumer]]
brokers = ["127.0.0.1:9092"]
topics = ["oceanic"]
data_format = "json"
Arguments:
Note: The remaining parameters can be consistent with the configuration example above.
brokers: Kafka's broker list
topics: Specifies the topic to write to in Kafka
data_format: The format of the data to be written
- Start Telegraf
telegraf -config /etc/telegraf/telegraf.conf
CnosDB
Deploy CnosDB
For detailed operation, please refer to:
Integration
Create Kafka Topic
- Enter the bin folder of kafka
- Execute command to create topic
./kafka-topics.sh --create --topic oceanic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --partitions 1 --replication-factor 1
Python simulates writing data to Kafka
- Write Code
import time
import json
import random
from kafka import KafkaProducer
def random_pressure():
return round(random.uniform(0, 10), 1)
def random_tempreture():
return round(random.uniform(0, 100), 1)
def random_visibility():
return round(random.uniform(0, 100), 1)
def get_json_data():
data = {}
data["pressure"] = random_pressure()
data["temperature"] = random_temp_cels()
data["visibility"] = random_visibility()
return json.dumps(data)
def main():
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['ip:9092'])
for _ in rang(2000):
json_data = get_json_data()
producer.send('oceanic', bytes(f'{json_data}','UTF-8'))
print(f"Sensor data is sent: {json_data}")
time.sleep(5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- Run Python script
python3 test.py
View data in Kafka topic
- Execute the following command to view the specified topic data
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic oceanic --from-beginning
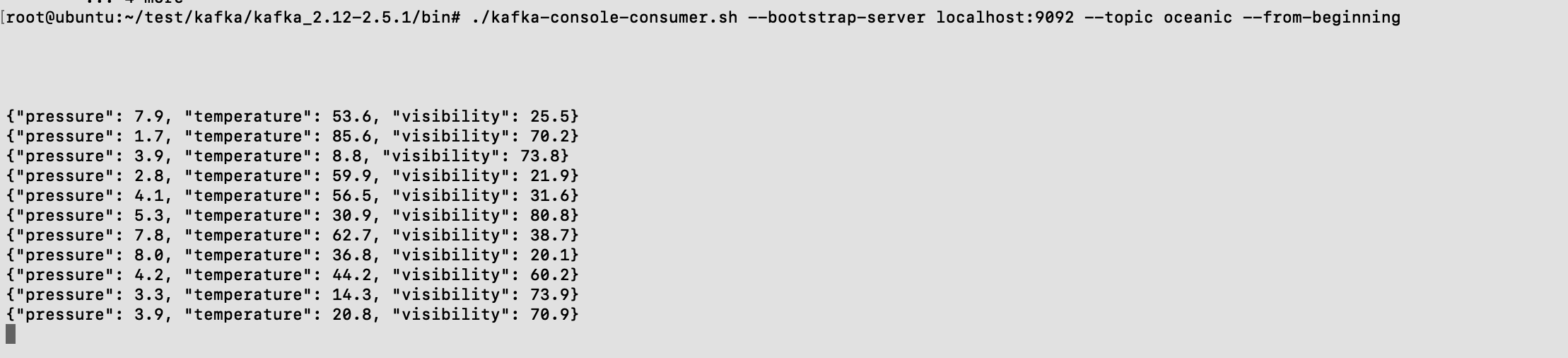
View data synchronized to CnosDB
- Connect to CnosDB using tools
cnosdb-cli
- Switch to the specified database
\c public
- View Data
select * from kafka_consumer;