Benchmark
To present CnosDB performance more intuitively, we do performance test of CnosDB and InfluxDB of the same time series database by using tsdb-comparisons.
Basic Information
| CnosDB | InfluxDB | |
|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0.1 | 1.8.10 |
| Implementation language | rust | go |
| Official website | www.cnosdb.com | https://www.influxdata.com |
Testing Environment
To avoid being affected by network bandwidth while better simulating multi- tenant scenarios, our service side server opens a virtual machine as service side machines, while the client machine opens two Benchmark clients simultaneously and writes data to different databases of the service side virtual machine, CanosDB, or InfluxDB
All tests run on our servers, with the following configurations:
Service side server:32 CPUs x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 5218 CPU @ 2.30GHz(memory:255.65 GB)
Virtual machine CPU allocates 16 cores.
Two disks in total, one is loaded into a virtual machine / opt- sdc1, performance Bench is as follows:
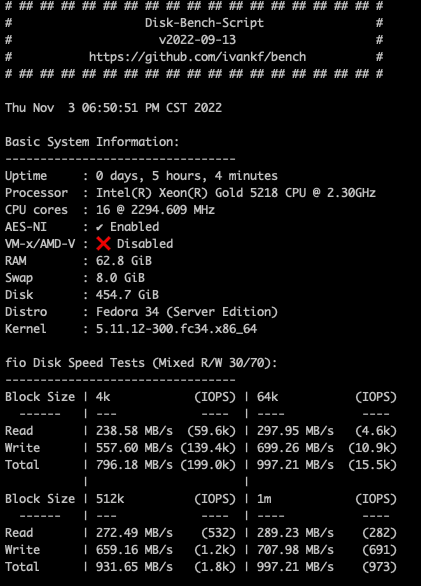
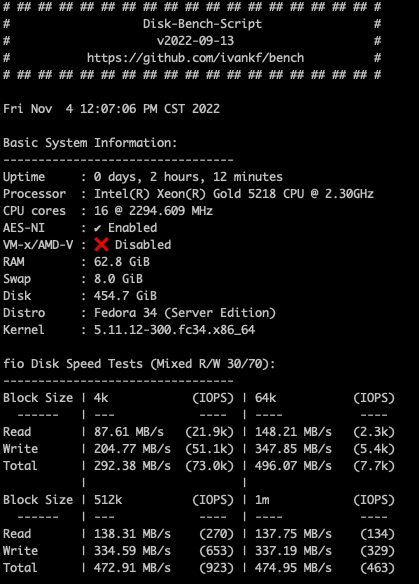
Other directory disk performance of virtual machines is as follows:
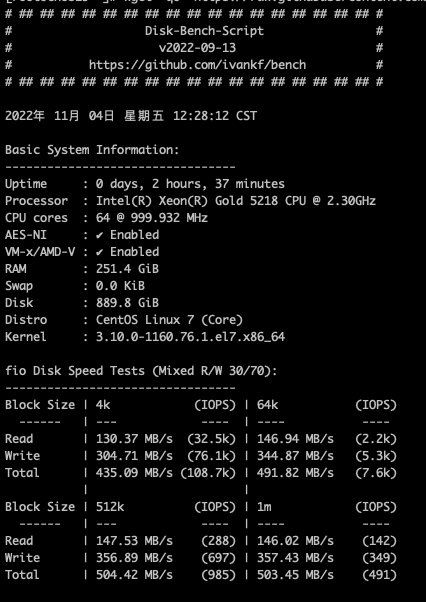
Client server: 32 CPUs x Intel (R) Xion (R) Gold 5218 CPU @ 2.30GHz (memory 256)
Disk performance Bench is as follows:
Configuration
The configuration of the CosDB is as follows:
[storage]
# Directory for summary: $path/summary/
# Directory for index: $path/index/$database/
# Directory for tsm: $path/data/$database/tsm/
# Directory for delta: $path/data/$database/delta/
path = '/opt/data/db'
max_summary_size = 134217728 # 128 * 1024 * 1024
max_level = 4
base_file_size = 16777216 # 16 * 1024 * 1024
compact_trigger = 4
max_compact_size = 2147483648 # 2 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024
dio_max_resident = 1024
dio_max_non_resident = 1024
dio_page_len_scale = 10
strict_write = false
[wal]
enabled = true
path = '/opt-sdc1/data/wal'
sync = false
[cache]
max_buffer_size = 10485760 # 10 * 1024 * 1024
max_immutable_number = 4
[log]
level = 'info'
path = 'data/log'
[security]
# [security.tls_config]
# certificate = "./config/tls/server.crt"
# private_key = "./config/tls/server.key"
InfluxDB is the default configuration except [data] and [meta]
[meta]
# Where the metadata/raft database is stored
dir = "/opt-sdc1/var/lib/influxdb/meta"
[data]
# The directory where the TSM storage engine stores TSM files.
dir = "/opt/var/lib/influxdb/data"
# The directory where the TSM storage engine stores WAL files.
wal-dir = "/opt-sdc1/var/lib/influxdb/wal"
Specific Steps
Install the db environment, go environment, etc. of the corresponding machine in advance, and ensure normal connection.
Install CnosDB:
Pull the code off GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/cnosdb/cnosdb.gitModify partial configurations in the
config/config.toml, runcargo run --release run --cpu 64Download InfluxDB, modify configurations in
etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf, runwget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.8.10_linux_amd64.tar.gz
tar xvfz influxdb-1.8.10_linux_amd64.tar.gz
./influxd run -config ../../etc/influxdb/influxdb.confTsdb-comparisons generate data
Pull the code off GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/cnosdb/tsdb-comparisons.gitCompile Running Generated Data
cd tsdb-comparisons/cmd/generate_data
go build
./generate_data --use-case="iot" --seed=123 --scale=100 --timestamp-start="2022-01-01T00:00:00Z" --timestamp-end="2023-01-01T00:00:00Z" --log-interval="50s" --format="influx" > <file_path>/data.txtTest CnosDB writes
cd tsdb-comparisons/cmd/load_cnosdb
go build
./load_cnosdb --do-abort-on-exist=false --do-create-db=false --gzip=false --file=<file_path>/data.txt --db-name=<db_name> --urls="http://<ip>:8902" --batch-size=<batch_size_num> --workers=<workers_num>Test InfluxDB writes
cd tsdb-comparisons/cmd/load_influx
go build
./load_influx --do-abort-on-exist=false --do-create-db=true --gzip=false --file=<file_path>/data.txt --db-name=<db_name> --urls="http://<ip>:8086" --batch-size=<batch_size_num> --workers=<workers_num>
Test Results
In our test scenario, InfluxDB can but do wrokers = 100(100 concurrent scenarios), with the test results as follows (row and metric units: 10,000):
| CnosDB | InfluxDB | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| batch-size | overall row/s | overall metric/s | overall row/s | overall metric/s |
| 20000 | 75 | 604 | ||
| 10000 | 68 | 538 | 54 | 420 |
| 5000 | 66 | 512 | 61 | 480 |
| 2500 | 53 | 420 | 57 | 450 |
| 1000 | 43 | 330 | 49 | 389 |
| 1 | 6 | 48 | 2.5 | 15 |
We take the data in Benchmark when database writing levels off which is valued at the sum of two clients.
When the batch-size is set to 20,000, InfluxDB returns an error on the client:
{"error":"engine: cache-max-memory-size exceeded: (1074767264/1073741824)"},
So we did not test the performance of InfluxDB in this case, but you can see that CnosDB is better than InfluxDB in most scenarios.
In addition, CnosDB supports higher concurrent numbers, and we also test the performance of CnosDB under workrs = 200 (200 concurrent scenarios). The results are as follows (row and metric units: 10,000):
| CnosDB | ||
|---|---|---|
| batch-size | overall row/s | overall metric/s |
| 20000 | 75 | 601 |
| 10000 | 75 | 607 |
| 5000 | 67 | 518 |
| 2500 | 60 | 463 |
| 1000 | 49 | 382 |
| 1 | 6 | 47 |
With the increase of concurrent numbers, performance in some scenarios will also be improved, and CnosDB performance has a higher ceiling.
Conclusion
- CnosDB has higher performance than InfluxDB in most cases.
- CnosDB can support higher concurrent, higher batch-size than InfluxDB.
- We do not compare with other time series databases that do not support Line Productol or transform line Protocol on the client, which is not fair for CnosDB and InfluxDB that writes directly to Line Protocol.