Architecture
The CnosDB architecture mainly includes two types of processes: CnosDB and CnosDB meta, named cnosdb and cnosdb-meta respectively. CnosDB supports online horizontal expansion of nodes. Supports metadata and data backup to ensure cluster stability. Support for most SQL syntax, using the built-in cnosdb-cli client can quickly and easily connect to CnosDB for query and import.
The following figure shows the architecture of CnosDB.
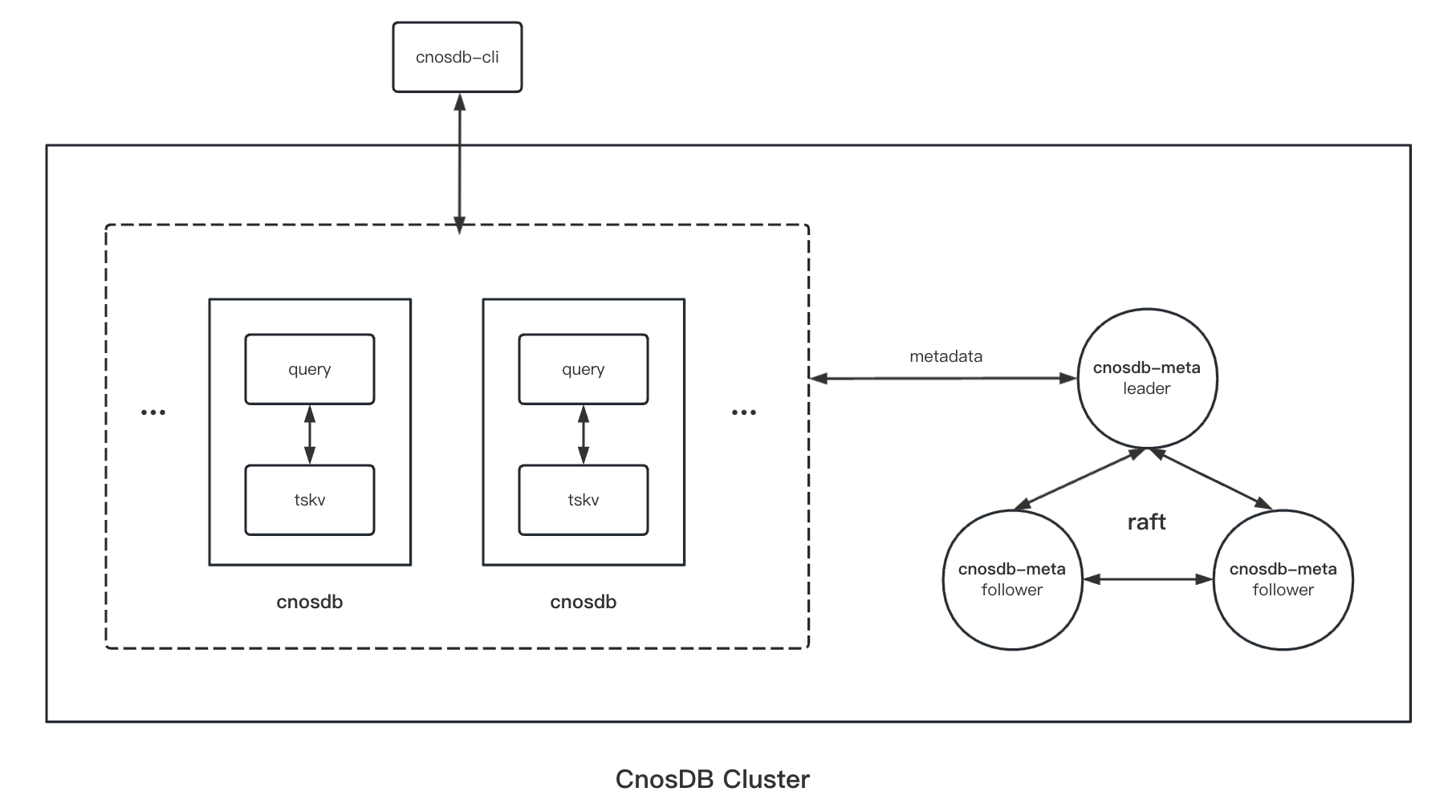
CnosDB meta
CnosDB meta ,the corresponding program named cnosdb-meta, the role is to maintain the consistency of the cluster. It stores metadata in the cluster, including information about the topology of the cluster, the distribution of replicas, and the distribution of data.
cnosdb-meta ,there are two roles: the cnosdb-meta leader and the cnosdb-meta follower, in which one cnosdb-meta is elected to be the leader through raft consistency protocol. The leader election requires more than half of the follower nodes to survive. Therefore, in a distributed cluster service, it is recommended to deploy 2n+1 cnosdb-meta services to ensure the high availability of the cluster.
CnosDB makes the following optimizations in the meta cluster:
- Cache and localize frequently accessed data.
- After the schema information is stored locally, subscribe to the schema version changes from the meta cluster to relieve the read pressure on the meta cluster.
- The meta cluster shares the leader pressure and provides a Follower/Read solution to optimize the read performance.
CnosDB
CnosDB, the corresponding program named cnosdb, is used to query and store data. cnosdb is internally divided into two services: query service and tskv storage service, which are the core of cnosdb.
Query : Query service, mainly responsible for client connection, query planning, sql analysis and other work. Tskv : Storage service, mainly responsible for the storage of data and the execution of sql physical plans.
Data management
In Cnosdb, the data management adopts the DB+Time_range shard rule. The number of shards is set by specifying the number of buckets when creating the database, and the time data is cut into Vnodes according to the set interval using the timeline property. Finally, each Vnode is dropped into a bucket for storage, as shown below.
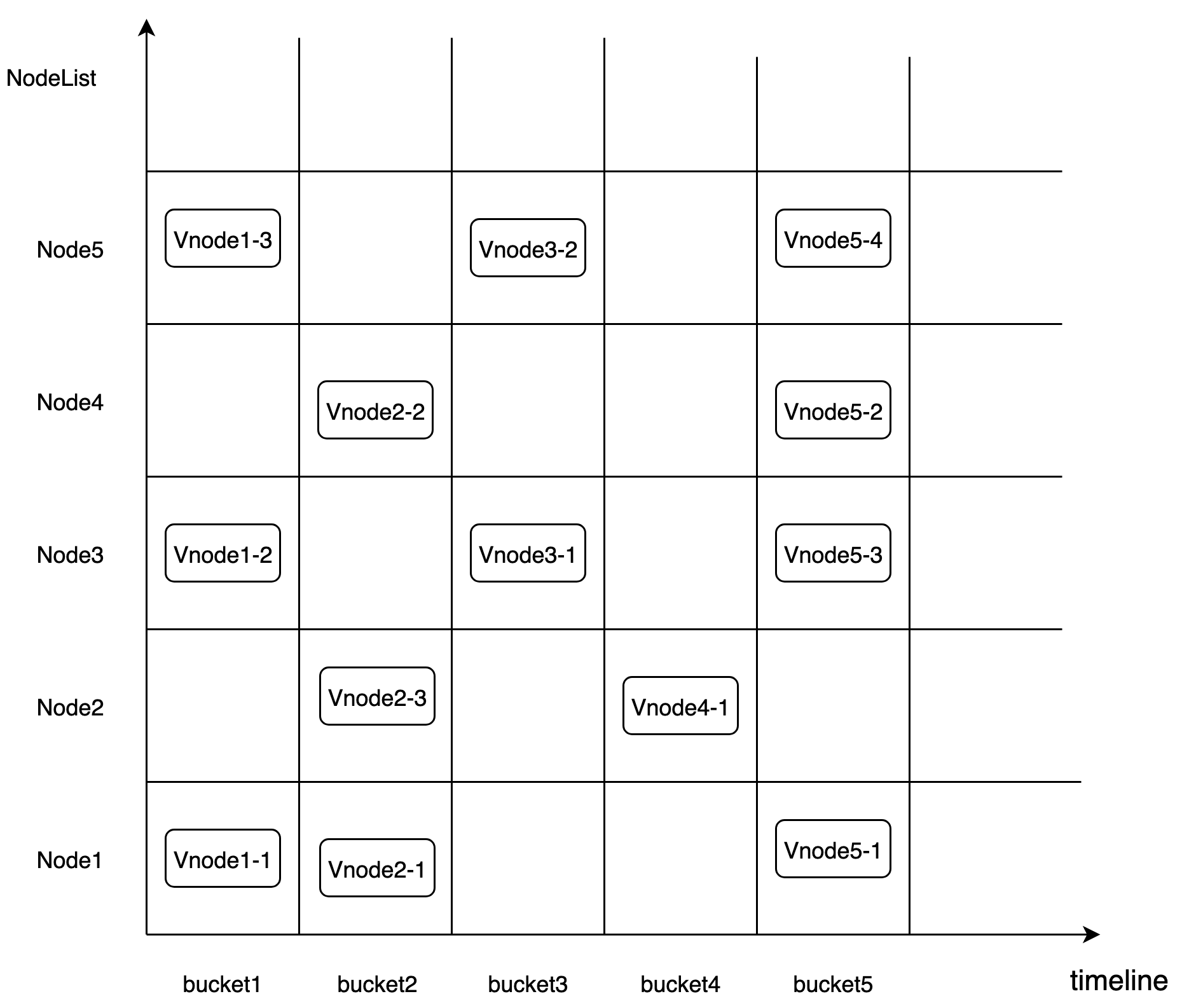
Bucket : A bucket is a logical unit, specified when the library is created. Each bucket contains the following main properties: < db, shardid, time_range, create_time, end_time, List< Vnode > >.
Vnode : A Vnode is a logical computing unit distributed to a specific Node, and it is also the smallest unit for data replication.
Replicaset : The high availability of data is maintained by the Data replicaset. Each db has multiple replication groups, which represent the number of replicas of data. A group of Vnodes in a bucket form a replicaset. All Vnodes in a replicaset have the same data and inverted index information.